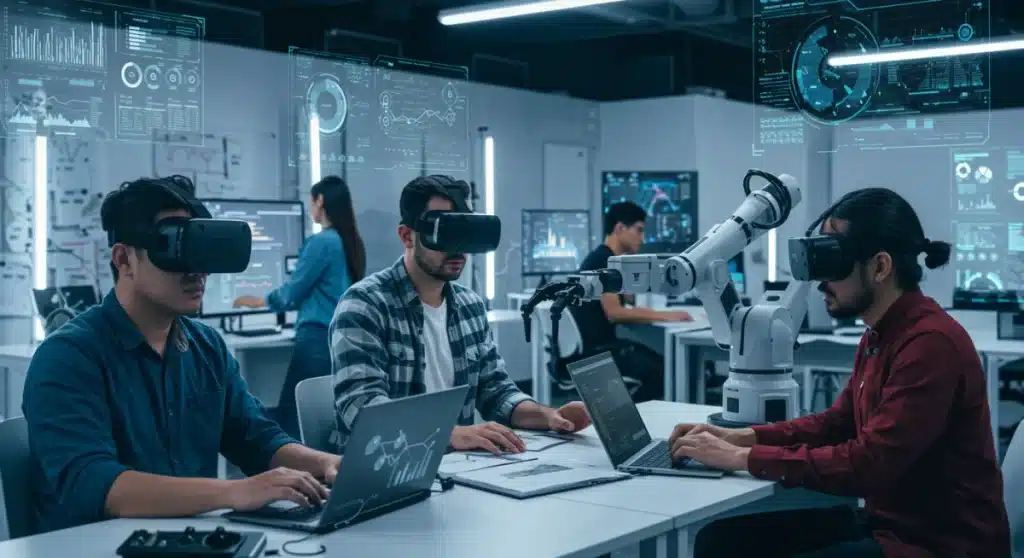
The 2025 outlook indicates that vocational training is undergoing a significant transformation due to the rapid evolution of technology, necessitating a focus on specific emerging tech skills to meet future workforce demands.
The landscape of work is continually evolving, and with it, the demands placed on the workforce. As we approach 2025, the need for specific emerging tech skills is not just a trend but a fundamental shift reshaping vocational training across the United States. This article delves into how three critical technological advancements are redefining what it means to be job-ready, offering invaluable insights for individuals and institutions alike.
The AI Revolution: Integrating Artificial Intelligence into Everyday Trades
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s an integral part of modern industries, from manufacturing to customer service. Vocational training programs must adapt to this reality, ensuring graduates possess the skills to work alongside and leverage AI tools. This integration isn’t about turning every vocational student into an AI developer, but rather equipping them with the practical knowledge to utilize AI in their respective fields.
Consider the impact on traditional trades. An electrician might use AI-powered diagnostics for smart home systems, while an automotive technician could employ AI tools for predictive maintenance on electric vehicles. The goal is to enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and create more sophisticated solutions within existing vocational roles.
Understanding AI Applications
Vocational students need to grasp the fundamental principles of AI and machine learning. This doesn’t require deep theoretical knowledge, but rather an understanding of how AI operates in practical scenarios.
- AI-powered diagnostics: Learning to interpret data from AI systems for troubleshooting.
- Automated process management: Understanding how AI streamlines workflows and repetitive tasks.
- Human-AI collaboration: Developing skills to work cooperatively with AI tools and systems.
The curriculum must evolve to include modules on AI literacy, ethical considerations of AI use, and hands-on experience with AI-driven applications. This ensures that vocational graduates are not just observers of the AI revolution but active participants, capable of harnessing its power to drive innovation and efficiency in their careers. The future workforce will be one that seamlessly integrates AI into daily operations, making this skill set indispensable.
Cybersecurity Fundamentals: Protecting Digital Assets in Every Sector
In an increasingly interconnected world, cybersecurity is paramount. Every industry, regardless of its primary function, now relies heavily on digital infrastructure and data. This makes cybersecurity not just a specialized IT field but a foundational skill essential for virtually all vocational roles. From healthcare records to manufacturing control systems, protecting digital assets is a shared responsibility.
Vocational training must instill a strong understanding of cybersecurity best practices, risk assessment, and incident response. This empowers individuals to safeguard sensitive information and maintain operational integrity within their organizations. The consequences of cyber breaches can be devastating, highlighting the urgent need for a cyber-aware workforce.
Key Cybersecurity Competencies
For vocational professionals, cybersecurity involves more than just knowing what a firewall is. It’s about understanding common threats and implementing basic protective measures.
- Data privacy and protection: Adhering to regulations and best practices for handling sensitive information.
- Network security basics: Recognizing vulnerabilities and implementing safeguards for local networks.
- Threat identification: Learning to spot phishing attempts, malware, and other common cyber threats.
Integrating cybersecurity into vocational programs means teaching students how to identify and mitigate risks relevant to their specific industry. For example, a student in hospitality management might learn about protecting customer data, while a manufacturing student focuses on securing industrial control systems. This tailored approach ensures that cybersecurity education is practical and directly applicable, creating a robust defense against digital threats across all vocational sectors. A proactive stance on cybersecurity training is crucial for the resilience of businesses and individuals alike.
Data Literacy and Analytics: Making Informed Decisions with Information
Data is often referred to as the new oil, and for good reason. Every interaction, transaction, and process generates valuable data that, when properly analyzed, can drive informed decision-making and innovation. Data literacy and analytics are therefore critical emerging tech skills that vocational training must emphasize. This involves not just collecting data but understanding how to interpret it, extract meaningful insights, and apply those insights to improve performance and outcomes.
Imagine a culinary student learning to analyze customer feedback data to refine menu offerings, or a construction worker using project data to optimize resource allocation and minimize waste. These applications demonstrate how data literacy transcends traditional boundaries, empowering vocational professionals to operate more strategically and efficiently. The ability to understand and utilize data transforms raw information into actionable intelligence.

Vocational programs need to move beyond basic spreadsheet skills and introduce students to data visualization tools, statistical thinking, and the principles of data-driven decision-making. This ensures that graduates are not just performing tasks but are actively contributing to the strategic success of their organizations by leveraging data effectively.
Practical Data Skills for Vocational Roles
Developing data literacy means equipping students with the tools to handle and interpret data relevant to their field. This includes understanding metrics, trends, and patterns.
- Data collection and organization: Learning effective methods for gathering and structuring data.
- Basic statistical analysis: Understanding averages, medians, and correlations to interpret data.
- Data visualization: Creating charts and graphs to communicate insights clearly.
The emphasis should be on practical application, allowing students to work with real-world datasets from their chosen vocational areas. This hands-on experience builds confidence and proficiency, preparing them to turn data into a competitive advantage. Data literacy is no longer an optional extra but a core competency for navigating the complexities of modern business and industry.
Reskilling and Upskilling: The Imperative for Continuous Learning
The rapid pace of technological change means that initial vocational training, no matter how comprehensive, will not suffice for an entire career. Reskilling and upskilling initiatives are therefore critical components of the 2025 outlook for vocational education. This goes beyond simply updating existing curricula; it involves creating flexible, accessible pathways for lifelong learning, enabling professionals to continuously acquire new emerging tech skills as they become relevant.
Government initiatives, industry partnerships, and educational institutions are increasingly recognizing the need for modular, stackable credentials that allow individuals to specialize or pivot their skill sets without having to restart their education from scratch. This agile approach to learning is essential for maintaining a competitive workforce and ensuring economic resilience in the face of technological disruption.
For individuals, embracing a mindset of continuous learning is paramount. This means actively seeking out opportunities for professional development, whether through online courses, workshops, or certifications. For employers, investing in employee training and development is no longer a luxury but a strategic necessity to retain talent and remain innovative. The future belongs to those who are willing to adapt and evolve their skill sets continuously.
Strategies for Lifelong Learning
Effective reskilling and upskilling require strategic planning and accessible resources. Both individuals and institutions play a role in fostering this culture.
- Micro-credentials: Earning specialized certifications for specific skills rather than full degrees.
- Online learning platforms: Utilizing digital resources for flexible and self-paced education.
- Industry-recognized certifications: Pursuing credentials valued by employers in specific tech domains.
The focus must be on creating a learning ecosystem that supports individuals at every stage of their career, providing them with the tools and opportunities to thrive in an ever-changing professional landscape. This proactive approach to skill development will be a defining characteristic of successful workforces in 2025 and beyond, ensuring that vocational training remains relevant and impactful.
The Role of Vocational Institutions: Adapting to New Demands
Vocational institutions are at the forefront of this transformation, tasked with preparing students for a future that is rapidly taking shape. Adapting to the demand for emerging tech skills requires more than just updating textbooks; it calls for a holistic re-evaluation of teaching methodologies, infrastructure, and industry partnerships. These institutions must become agile hubs of innovation, sensitive to market demands and capable of quickly integrating new technologies into their programs.
This involves significant investment in state-of-the-art equipment, training for instructors, and the development of curricula that are both rigorous and responsive. Collaborations with local businesses and tech companies are crucial, providing real-world experience for students and ensuring that the skills taught are directly aligned with industry needs. The success of vocational training in 2025 will largely depend on its ability to forge strong connections between education and employment.
Furthermore, vocational institutions have a responsibility to counsel students on the evolving career landscape, guiding them towards pathways that offer long-term growth and stability. This includes highlighting the importance of soft skills alongside technical competencies, as effective communication, problem-solving, and adaptability remain critical in any tech-driven role. Preparing students for a dynamic future means equipping them with a versatile and resilient skill set.
Institutional Adaptations for Future Readiness
To remain relevant, vocational institutions must embrace several key changes in their operational and educational models.
- Curriculum modernization: Regularly updating courses to reflect the latest technological advancements.
- Instructor training: Providing ongoing professional development for educators in new tech fields.
- Industry collaboration: Partnering with businesses for internships, apprenticeships, and curriculum input.
By proactively addressing these challenges, vocational institutions can ensure they remain vital engines of economic growth and social mobility, providing accessible and high-quality education that truly prepares individuals for the demands of the modern workforce. Their ability to innovate and adapt will be a cornerstone of future workforce development.
Policy and Funding: Supporting the Next Generation of Skilled Workers
The transformation of vocational training to meet the demands of emerging tech skills cannot happen in a vacuum. It requires robust support from policymakers and adequate funding mechanisms. Government bodies, at both federal and state levels, play a crucial role in creating an environment that fosters innovation in education and workforce development. This includes allocating resources for equipment upgrades, instructor training, and the development of new, tech-focused curricula.
Policies that incentivize industry partnerships and provide funding for apprenticeship programs are particularly effective. These mechanisms bridge the gap between classroom learning and real-world application, ensuring that students gain practical experience with the latest technologies. Additionally, government initiatives can help promote awareness of vocational pathways, challenging outdated perceptions and highlighting the high-tech, high-demand nature of many skilled trades.
Public-private partnerships are also vital, allowing private sector expertise and resources to augment public educational efforts. This collaborative approach ensures that vocational training programs are nimble enough to respond to rapidly changing industry needs, producing graduates who are immediately employable and capable of contributing to economic growth. Investing in vocational education is an investment in the nation’s future workforce and its global competitiveness.
Government and Industry Support Areas
Effective policy and funding strategies focus on several key areas to maximize the impact on vocational training.
- Grants for tech upgrades: Providing financial aid for institutions to acquire modern equipment.
- Tax incentives for employers: Encouraging companies to offer apprenticeships and training.
- Workforce development programs: Funding initiatives that connect job seekers with training and employment.
By prioritizing policy frameworks and funding models that support the integration of emerging tech skills into vocational training, the United States can ensure a skilled, adaptable, and competitive workforce for 2025 and beyond. This strategic investment is fundamental to addressing future labor market demands and fostering sustained economic prosperity.
| Key Skill Area | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| AI Integration | Utilizing AI tools for diagnostics, automation, and decision-making in various trades. |
| Cybersecurity Fundamentals | Protecting digital assets and understanding cyber threats across all vocational sectors. |
| Data Literacy & Analytics | Interpreting data to drive informed decisions and improve operational efficiency. |
| Continuous Learning | Embracing lifelong education through reskilling and upskilling for career adaptability. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Emerging Tech Skills
The most critical emerging tech skills for vocational training by 2025 include AI integration, cybersecurity fundamentals, and data literacy and analytics. These skills are becoming essential across a wide range of industries, moving beyond traditional IT roles to impact virtually every trade and profession, ensuring workers are prepared for a technologically advanced workplace.
AI integration is relevant to non-tech vocational careers by enabling professionals to use AI-powered tools for enhanced efficiency and decision-making. For instance, mechanics can use AI for vehicle diagnostics, or construction workers can leverage AI for project management and site analysis, streamlining tasks and improving outcomes in their respective fields.
Cybersecurity is fundamental for all vocational roles because nearly every industry relies on digital systems and data. Protecting sensitive information and maintaining operational integrity from cyber threats is a universal responsibility. Understanding basic cybersecurity practices helps prevent breaches that could lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage across all sectors.
For vocational professionals, data literacy means the ability to collect, interpret, and use data to make informed decisions. This skill allows them to identify trends, optimize processes, and improve results in their specific trades. It transforms raw information into actionable insights, making professionals more strategic and efficient in their daily work and long-term planning.
Vocational training institutions can adapt by modernizing curricula, investing in advanced equipment, providing continuous training for instructors, and fostering strong partnerships with industries. These adaptations ensure that programs remain relevant, offering hands-on experience with the latest technologies, and preparing graduates with the practical skills demanded by the evolving job market.
Conclusion
The 2025 outlook unequivocally points to a future where vocational training is intrinsically linked to the mastery of emerging tech skills. AI integration, cybersecurity fundamentals, and data literacy are not merely buzzwords but essential competencies that will define career readiness. For individuals, this necessitates a commitment to continuous learning and adaptability. For educational institutions and policymakers, it demands proactive investment and strategic partnerships to ensure the workforce is equipped with the tools to thrive in an increasingly digital world. Embracing these technological shifts is not an option but a necessity for sustained professional and economic success.


 Federal Loan Forgiveness Programs: Key Updates for U.S. Professionals
Federal Loan Forgiveness Programs: Key Updates for U.S. Professionals  STEM Education Initiatives: New K-12 Opportunities in the U.S.
STEM Education Initiatives: New K-12 Opportunities in the U.S.  Top 6 In-Demand Certifications for U.S. Job Seekers
Top 6 In-Demand Certifications for U.S. Job Seekers