The future of labor rights in America is shaped by emerging labor movements advocating for fair wages, increased political advocacy, and protections against automation as workers unite to fight for their rights.
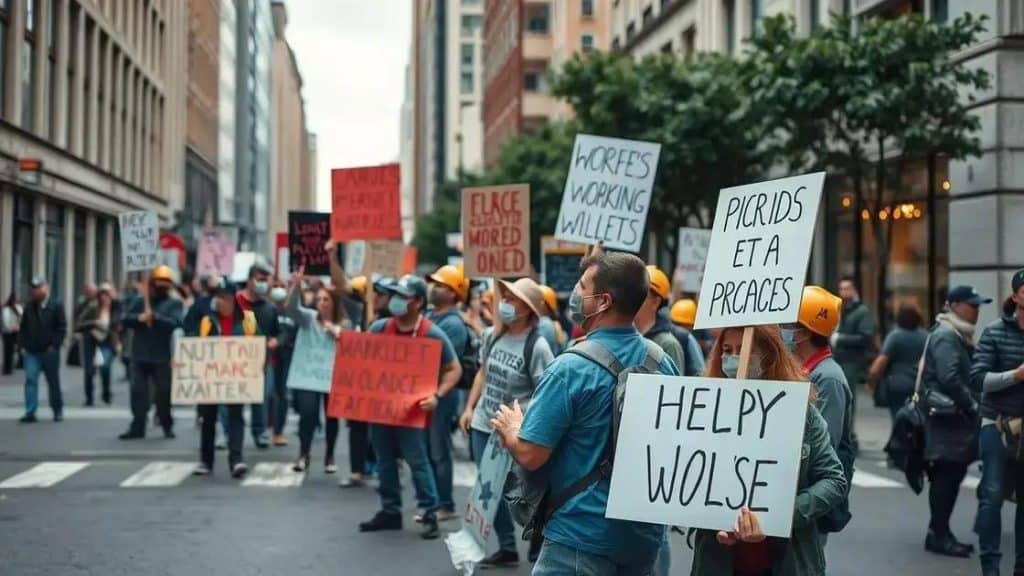
Organized labor stages nationwide economic protests to draw attention to critical issues affecting workers today. But why are these protests gaining momentum? Join me as we explore the reasons behind this wave of activism and its implications for the workforce.
The history of organized labor in the U.S.
The history of organized labor in the U.S. is a tale of struggle, resilience, and the fight for workers’ rights. Over the years, labor movements have played a crucial role in shaping the workplace we know today.
The Early Days
In the 19th century, workers faced harsh conditions, long hours, and minimal pay. The first labor unions began to form as workers sought to gain better treatment. These groups organized strikes, demanding changes that would benefit their lives.
Key Strikes and Movements
Some significant events include:
- The Great Railroad Strike of 1877
- The Haymarket Affair of 1886
- The Pullman Strike of 1894
Each of these movements highlighted the need for collective bargaining and drew public attention to labor issues.
In the early 20th century, the formation of the American Federation of Labor (AFL) marked a significant turning point. Under the leadership of Samuel Gompers, the AFL focused on skilled trades and fought for higher wages and better working conditions.
Legislation for Workers
The progress of organized labor led to essential legislation. Acts like the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 set the groundwork for workers’ rights in the U.S. This act established minimum wage and overtime pay, changing the landscape of labor practice.
As the decades went on, the union movement continued to evolve, addressing issues of gender, race, and the changing nature of work. Unions began to include a more diverse membership, reflecting the workforce’s composition.
Today, labor unions remain vital in protecting workers and advocating for rights. Their history shows the importance of unity and strength in numbers.
Key issues driving economic protests today
Today, several key issues are driving economic protests across the country. These concerns reflect the ongoing struggles workers face in their daily lives. Understanding these issues is crucial to grasping the current labor movement’s landscape.
Wage Inequality
One of the most significant factors is wage inequality. Many workers earn far less than what they need to survive, while top executives receive enormous paychecks. This disparity has led to widespread frustration and calls for fairer wages.
- Minimum wage not keeping up with inflation
- Pay gap between genders and races
- Struggles of low-income workers
A growing number of people believe that every worker deserves a living wage, prompting protests demanding higher pay and better benefits.
Job Security
An increasing number of workers feel insecure in their jobs. The rise of contract work and gig economy positions has made many employees vulnerable. Often, they lack benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans.
Moreover, repeating layoffs and automation threaten job stability. Workers are rallying to demand more secure employment and consistent hours.
Healthcare Access
Healthcare remains a pressing issue for many Americans. Lack of access to affordable healthcare is a leading concern fueling protests. Many workers are advocating for:
- Universal healthcare
- Lower drug prices
- Better workplace health programs
When healthcare is unaffordable, workers face tough choices that affect their wellbeing and productivity.
As protests continue to grow, they reflect broader demands for social and economic justice. Workers are united in their quest for change, resonating with the need for a better future.
Major events in recent labor movements

Recent labor movements have been marked by significant events that highlight the ongoing struggle for workers’ rights. These events showcase worker solidarity and the push for social justice.
The Fight for Higher Wages
In many cities across the United States, workers from various sectors have organized strikes demanding higher wages. One notable example is the fast-food workers’ strike in 2019.
- Workers demanded a $15 minimum wage.
- The movement was supported by labor unions and social justice groups.
- Protests occurred in over 300 cities.
This strike generated widespread media attention and renewed conversations about living wages.
Teacher Strikes Across the Country
In 2018 and 2019, teachers in several states went on strike demanding better pay and adequate school funding. These protests occurred in states like West Virginia, Arizona, and Oklahoma, highlighting education inequalities.
Some key aspects of these strikes include:
- Increased salaries for educators
- Funding for classroom supplies
- Better healthcare benefits
The teachers’ strikes not only focused on pay but also on the overall quality of education for students.
The Rise of Gig Worker Activism
As the gig economy grows, workers from companies like Uber and Lyft have started advocating for better treatment and rights. In recent years, gig workers have organized protests to demand:
- Benefits like health insurance
- Fair pay for rides and deliveries
- Recognizing them as employees rather than independent contractors
This activism reflects a fundamental shift in how workers view their rights in the modern economy.
The recent events in labor movements underscore a strong desire for change among workers in the U.S. Their collective actions are shaping the future of labor rights.
Challenges faced by organized labor
Organized labor faces numerous challenges in today’s economy, making it vital for unions to adapt and innovate. The landscape for labor movements is ever-changing, influenced by various social and economic factors.
Declining Union Membership
Over the years, union membership has steadily declined. This decrease poses a significant challenge for organized labor.
- Industries are moving towards non-unionized labor.
- Younger workers may not see the value of joining unions.
- Workers are often unaware of their rights regarding unionization.
These factors create an environment where fewer workers are represented, weakening labor’s collective bargaining power.
Legislative and Political Barriers
Political challenges are another obstacle. In many states, laws have been enacted that weaken unions. This includes:
- Right-to-work laws that limit union funding
- Legislation that makes organizing difficult
- A lack of support from political leaders
These legal hurdles significantly impact the effectiveness of unions in advocating for workers’ rights.
Workplace Automation
As technology advances, automation continues to replace many jobs traditionally held by union members. This shift creates uncertainty for workers, as they fear job loss.
Workers are now facing the need to adapt to new skills and technology quickly. Many unions are advocating for training programs to prepare workers for the future job market.
Public Perception
Public perception of unions also plays a big role. While unions have historically fought for workers’ rights, some people view them negatively, associating them with strikes and disruption.
This perception can hinder union efforts to gain support from the community and potential members. To combat this, labor organizations are working hard to showcase their positive contributions to society.
Overall, organized labor must navigate these challenges to continue advocating for the rights and needs of workers in the changing economic landscape.
The future of labor rights in America
The future of labor rights in America is a topic of great discussion and importance. With evolving economic conditions and social expectations, the landscape of labor rights is changing rapidly.
Emerging Trends in Labor Movements
Recently, there has been a resurgence in labor movements, particularly among younger workers. Many are advocating for fair wages, better working conditions, and a voice in the workplace. This shift signals a new era for unions and organized labor.
- Union membership is seeing a slow increase, particularly in the tech and service industries.
- Younger workers are more open to unionization compared to previous generations.
- There is a growing awareness around social justice issues in the workplace.
As these trends continue, they will likely lead to stronger unions that better represent their members.
Technological Impact on Work
Technology is transforming the way people work. Automation, remote working, and gig economy jobs are on the rise. This transformation presents challenges and opportunities for labor rights.
Workers now need to adapt to new forms of employment, which often lack traditional benefits. Many labor organizations are advocating for:
- Stronger protections for gig workers
- Access to healthcare for all workers
- Training programs to help workers transition to new roles
These initiatives will be crucial for ensuring that all workers can thrive in a changing economy.
Legislative Changes and Advocacy
Political advocacy will play a significant role in shaping labor rights. Workers and unions are increasingly engaging in the political process to influence legislation.
Support for policies like:
- The PRO Act, which seeks to protect the rights of union organizers
- Increased funding for worker training programs
- Stricter regulations for gig economy companies
These efforts can help create a fairer and more equitable workforce, directly impacting the future of labor rights in America.
Overall, as workers continue to mobilize and advocate for their rights, the future of labor rights looks promising. The movement is fueled by a new generation of workers determined to ensure that their voices are heard and respected.
In conclusion, the future of labor rights in America looks hopeful as workers become more engaged in advocating for their rights. The rise of new labor movements signals a renewed interest in unionization and fair treatment. With challenges like wage inequality and automation, it is essential for unions to adapt and fight for the needs of all workers. Political advocacy will be crucial in pushing for policies that strengthen labor rights. As we move forward, a united workforce can create meaningful change that benefits both workers and the economy.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Labor Rights in America
What are the key challenges facing organized labor today?
Some key challenges include declining union membership, political barriers, workplace automation, and public perception of unions.
How are younger workers influencing labor movements?
Younger workers are more likely to join unions and advocate for fair wages, better working conditions, and social justice issues.
What role does technology play in the future of labor rights?
Technology is changing job roles and creating new types of employment, which leads to a need for stronger protections and training programs for workers.
Why is political advocacy important for worker’s rights?
Political advocacy helps to push for policies that strengthen labor rights and protect workers, ensuring their voices are heard in legislative decisions.


 Atlantic Hurricane Season 2024: Experts Forecast 15 Named Storms
Atlantic Hurricane Season 2024: Experts Forecast 15 Named Storms  U.S. Consumer Price Index Rises 3.5% Annually: What It Means
U.S. Consumer Price Index Rises 3.5% Annually: What It Means  Climate Change Executive Order: New Regulations Mid-June
Climate Change Executive Order: New Regulations Mid-June