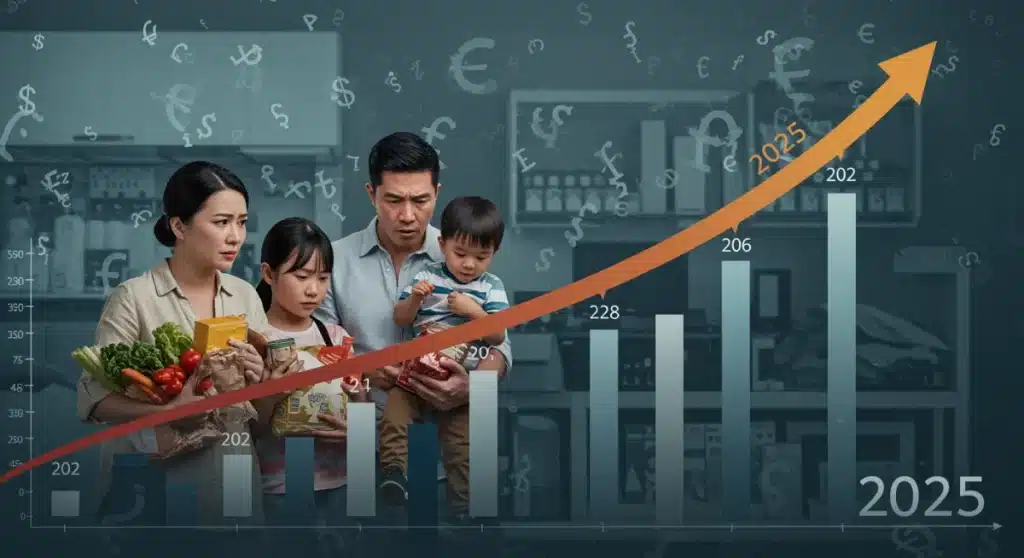
Current inflation trends are reshaping the economic landscape, significantly influencing consumer purchasing power; understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating financial stability into 2025.
Understanding inflation trends 2025 is more critical than ever for every American household. The economic forces at play today are complex, directly influencing how far your dollar stretches and what you can afford, making informed financial decisions paramount as we look towards the near future.
Analyzing Current Inflation Drivers and Their Persistence
The current inflationary environment is a multifaceted phenomenon, driven by a confluence of global and domestic factors. While some drivers, such as supply chain disruptions, have begun to ease, others demonstrate remarkable persistence, shaping the economic outlook for the coming years. Understanding these core drivers is essential to anticipate their continued influence on consumer purchasing power.
One significant contributor has been the unprecedented fiscal and monetary stimulus injected into the economy during the pandemic. This surge in liquidity, coupled with robust consumer demand, created an imbalance that pushed prices upward. Additionally, geopolitical events, particularly conflicts in key resource-producing regions, have led to spikes in energy and food prices, which permeate through nearly every sector of the economy.
Global Supply Chain Dynamics
While often cited, the intricacies of global supply chains continue to present challenges. Although some bottlenecks have resolved, new ones emerge, influenced by shifting geopolitical landscapes and localized disruptions. Manufacturers face increased costs for raw materials and transportation, which are inevitably passed on to consumers.
- Labor Shortages: Persistent labor market tightness in critical sectors contributes to higher wage demands, fueling cost-push inflation.
- Energy Price Volatility: Global oil and gas markets remain susceptible to geopolitical tensions, directly impacting transportation and production costs.
- Raw Material Scarcity: Certain key raw materials continue to experience supply constraints, driving up input costs for various industries.
The persistence of these drivers suggests that while the pace of inflation may moderate, a return to pre-pandemic price stability might be a gradual process, requiring consumers to adapt to a new normal of potentially higher costs for goods and services.
Projected Inflation Trajectories for 2025
Forecasting inflation is an inexact science, yet economic models and expert consensus point towards a continued, albeit moderated, inflationary environment into 2025. The consensus suggests that while the peak inflation rates observed in recent years are unlikely to recur, prices will not necessarily return to their previous levels, implying a sustained higher cost of living.
Central banks, like the Federal Reserve, are actively using monetary policy tools, primarily interest rate adjustments, to bring inflation back to their target levels. The effectiveness and timing of these policies will be crucial in shaping the trajectory. However, the lag effect of monetary policy means that decisions made today will only fully manifest their impact in the coming quarters and years.
Federal Reserve’s Stance and Market Expectations
The Federal Reserve has clearly communicated its commitment to price stability. Their actions, including a series of interest rate hikes, are designed to cool demand and reduce inflationary pressures. Market expectations for 2025 suggest that while rate hikes may plateau, rates will likely remain elevated compared to the ultra-low levels seen in the past decade.
- Interest Rate Stability: Many analysts predict a period of interest rate stability in 2025, following aggressive tightening cycles.
- Inflation Target: The Fed’s 2% inflation target remains a primary goal, guiding future policy decisions.
- Economic Growth: Balancing inflation control with maintaining healthy economic growth will be a key challenge for policymakers.
Overall, analysts expect a gradual deceleration of inflation, but the journey back to target levels will be influenced by a myriad of unpredictable factors, including global economic stability and domestic policy responses. Consumers should prepare for an environment where price increases, while slower, are still present.
Impact on Consumer Purchasing Power: A Detailed Look
The most tangible effect of sustained inflation is the erosion of consumer purchasing power. As prices for goods and services rise, each dollar buys less, directly impacting household budgets and living standards. This effect is particularly pronounced for essential items, disproportionately affecting lower and middle-income households.
The purchasing power of wages and savings is diminished, forcing consumers to make difficult choices about their spending. Discretionary spending often takes a hit first, as households prioritize necessities like food, housing, and transportation. This shift in spending patterns can have broader implications for economic growth, as consumer spending is a major component of GDP.
Real Wage Growth vs. Inflation
A critical indicator of consumer well-being is the comparison between wage growth and inflation. If wages do not keep pace with rising prices, consumers experience a decline in real income. While some sectors have seen significant wage increases, for many, these gains have been insufficient to offset the higher cost of living.
- Essential Goods: Prices for food, housing, and energy have seen some of the most significant increases, directly impacting daily living costs.
- Savings Erosion: The real value of savings held in low-interest accounts diminishes during periods of high inflation.
- Debt Burden: For those with variable-rate debt, higher interest rates, a tool used to combat inflation, can increase monthly payments.
The cumulative effect of reduced purchasing power extends beyond immediate spending, impacting long-term financial planning, retirement savings, and the ability to achieve financial milestones. Consumers will need to be strategic in managing their finances to mitigate these effects.
Sector-Specific Inflationary Pressures in 2025
While inflation has a broad impact, certain sectors are experiencing, and are projected to continue experiencing, more intense inflationary pressures than others. Understanding these sector-specific dynamics can help consumers and businesses anticipate where price increases will be most noticeable and adjust accordingly. Housing, energy, and healthcare are typically among the most sensitive areas.
For instance, the housing market, influenced by high demand, limited supply, and rising interest rates, has seen significant price appreciation. Energy costs, tied to global geopolitical events and supply-demand imbalances, remain volatile. Healthcare expenses, driven by technological advancements, administrative costs, and an aging population, continue their upward trend.

Key Sectors to Watch
Monitoring these sectors provides insight into where household budgets will be most strained. The interconnectedness of these areas means that price increases in one can quickly propagate to others, creating a ripple effect across the economy.
- Housing: Rent and mortgage costs are expected to remain elevated, though perhaps with slower growth than in previous years.
- Energy: Global events will continue to dictate fuel and utility price stability, posing ongoing challenges for consumers.
- Food: Supply chain issues, weather patterns, and labor costs will continue to influence grocery bills.
- Healthcare: Costs are expected to rise due to demand, innovation, and an aging demographic.
These sector-specific pressures mean that consumers will need to adopt targeted strategies to manage their expenses. Budgeting, seeking alternatives, and advocating for policy changes can all play a role in mitigating the impact of these concentrated price increases.
Strategies for Consumers to Mitigate Inflation’s Effects
In an inflationary environment, proactive financial planning and strategic consumption become paramount for consumers. While macroeconomic forces are largely beyond individual control, there are tangible steps households can take to protect their purchasing power and maintain financial stability. These strategies range from optimizing budgets to exploring investment opportunities that offer inflation hedges.
One of the most immediate actions is to meticulously review and adjust household budgets. Identifying areas where spending can be reduced or optimized is crucial. This might involve cutting back on non-essential items, seeking out sales, or finding more cost-effective alternatives for everyday necessities. Every dollar saved or spent more wisely contributes to mitigating the erosion of purchasing power.
Financial Planning and Investment Approaches
Beyond budgeting, strategic financial planning can offer long-term protection. This includes exploring investments that have historically performed well during inflationary periods and ensuring debt is managed effectively, especially variable-rate loans.
- Budget Optimization: Regularly review and adjust spending habits to prioritize essential goods and services.
- Debt Management: Prioritize paying down high-interest debt, especially variable-rate loans, to reduce exposure to rising interest costs.
- Inflation-Hedge Investments: Consider investments like real estate, commodities, or Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) that may offer protection against inflation.
- Income Growth: Seek opportunities for career advancement, skill development, or additional income streams to increase earnings.
By adopting a combination of these strategies, consumers can build greater resilience against the persistent effects of inflation. It requires discipline and a willingness to adapt, but the payoff is enhanced financial security in a challenging economic landscape.
Policy Responses and Their Expected Influence on 2025 Outlook
Governmental and central bank policy responses are pivotal in shaping the future trajectory of inflation and its ultimate impact on consumers. These policies aim to either curb inflationary pressures or provide support to households struggling with rising costs. Understanding their potential influence is key to anticipating the economic landscape of 2025.
Monetary policy, primarily executed by the Federal Reserve, involves adjusting interest rates and controlling the money supply. Higher interest rates are designed to cool demand and make borrowing more expensive, thereby slowing down economic activity and reducing price pressures. Fiscal policy, managed by the government, includes taxation, spending, and direct aid programs, which can also influence inflation and consumer well-being.
Effectiveness of Current Policies
The effectiveness of these policies in 2025 will depend on various factors, including the global economic environment, consumer and business confidence, and the responsiveness of supply chains. Policymakers face the delicate task of taming inflation without triggering a significant economic downturn.
- Monetary Policy Lag: The full effects of current interest rate hikes will continue to unfold into 2025, potentially further moderating inflation.
- Fiscal Spending Adjustments: Government spending decisions, particularly those related to infrastructure and social programs, will influence aggregate demand.
- Regulatory Environment: Changes in regulations, especially concerning energy, trade, and labor, could impact production costs and prices.
Ultimately, the interplay between these policy responses and underlying economic conditions will determine the extent to which inflation moderates and how consumer purchasing power is affected. A balanced and adaptive approach from policymakers will be crucial for fostering a stable economic environment.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Inflation Drivers | Global supply chains, labor shortages, and energy prices continue to fuel inflationary pressures into 2025. |
| 2025 Projections | Inflation is expected to moderate but remain above pre-pandemic levels, influenced by Federal Reserve policies. |
| Consumer Impact | Purchasing power erosion likely continues, requiring strategic budgeting and financial planning from households. |
| Mitigation Strategies | Consumers can employ budgeting, debt management, and inflation-hedging investments to safeguard finances. |
Frequently Asked Questions About 2025 Inflation
In 2025, inflation will likely be driven by persistent supply chain challenges, ongoing labor market tightness leading to wage pressures, and potential volatility in global energy markets. Geopolitical events could also continue to play a significant role in influencing commodity prices and overall economic stability, affecting various sectors.
Inflation will continue to erode the purchasing power of the average American household, meaning their money buys less goods and services. This impact will be particularly noticeable in essential categories like groceries, housing, and transportation, requiring households to adjust budgets and spending habits to maintain their living standards.
The Federal Reserve will continue its efforts to achieve price stability, likely maintaining a cautious stance on interest rates. While aggressive hikes might be behind us, the Fed will monitor economic data closely, adjusting monetary policy as needed to guide inflation towards its 2% target without stifling economic growth, balancing these critical objectives.
Sectors most affected by inflationary pressures in 2025 are projected to include housing, due to continued demand and supply constraints; energy, susceptible to global geopolitical events; and healthcare, influenced by rising costs of innovation and an aging population. Food prices will also remain sensitive to various supply chain and environmental factors.
Consumers can mitigate inflation’s effects by optimizing their budgets, prioritizing debt reduction (especially variable-rate loans), and exploring investments that historically perform well during inflationary periods, such as real estate or commodities. Seeking opportunities for income growth and making informed purchasing decisions are also crucial for financial resilience.
Conclusion
The journey through current inflation trends 2025 and their projected impact on consumer purchasing power presents a complex economic landscape. While a complete return to pre-pandemic price levels is unlikely, understanding the persistent drivers, anticipated trajectories, and sector-specific pressures empowers consumers to make informed financial decisions. Proactive budgeting, strategic investments, and awareness of policy responses are crucial tools for navigating an evolving economic environment and safeguarding individual financial well-being.


 2026 Housing Market Forecast: 8% Home Price Growth & Mortgage Rate Shifts
2026 Housing Market Forecast: 8% Home Price Growth & Mortgage Rate Shifts  Maximize 401(k) Contributions: Strategies for Optimal Retirement
Maximize 401(k) Contributions: Strategies for Optimal Retirement  Navigating 2026 Inflation: Protect Your Investments from 3.5% Rate
Navigating 2026 Inflation: Protect Your Investments from 3.5% Rate