New STEM education initiatives are set to transform U.S. K-12 learning, providing students with enhanced opportunities and crucial skills for future success in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
The landscape of education in the United States is constantly evolving, with a significant push towards equipping younger generations with the skills necessary for tomorrow’s challenges. Among these pivotal shifts, STEM education initiatives are taking center stage, promising to redefine learning experiences for K-12 students across the nation. These new opportunities, beginning in 2026, are designed to ignite curiosity, foster critical thinking, and prepare students for careers in high-demand fields.
The imperative for enhanced STEM education
The call for robust STEM education has never been louder. As technology advances at an unprecedented pace, the demand for professionals skilled in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics continues to grow exponentially. Recognizing this, U.S. educational policymakers and innovators are implementing comprehensive strategies to strengthen STEM learning from kindergarten through twelfth grade.
These initiatives are not merely about introducing more science classes; they represent a fundamental rethinking of how these subjects are taught and integrated into the curriculum. The goal is to move beyond rote memorization, encouraging hands-on exploration, problem-solving, and collaborative learning. This holistic approach aims to cultivate a generation of innovators, thinkers, and problem-solvers.
Bridging the skills gap
One of the primary drivers behind these new programs is the persistent skills gap in critical industries. Many sectors, from advanced manufacturing to cybersecurity, struggle to find qualified candidates. By bolstering STEM education at an early age, the aim is to create a robust pipeline of talent capable of meeting these future workforce needs.
- Early exposure: Introducing STEM concepts early builds foundational knowledge.
- Practical application: Emphasizing real-world problem-solving connects learning to practical outcomes.
- Interdisciplinary approach: Integrating subjects like coding into art or history makes learning more engaging.
The new initiatives beginning in 2026 are poised to make significant inroads in addressing this gap by fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation for STEM disciplines among K-12 students. This proactive stance ensures that the U.S. remains competitive on the global stage, powered by a skilled and innovative workforce.
In conclusion, the enhanced focus on STEM education is a strategic investment in the nation’s future. By equipping students with essential skills, these initiatives promise to bridge critical workforce gaps and foster a culture of innovation from an early age.
Key components of the 2026 STEM curriculum
The upcoming STEM curriculum rollout in 2026 introduces several innovative components designed to make learning more effective and engaging. These elements are a direct response to feedback from educators, industry leaders, and educational researchers, aiming to create a dynamic learning environment that prepares students for complex challenges.
A significant focus is placed on project-based learning, where students tackle real-world problems through scientific inquiry and engineering design. This approach fosters critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration, moving beyond traditional textbook learning to active discovery.
Integrated learning modules
The new curriculum emphasizes integrated learning modules that break down the traditional silos between science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. For instance, a lesson on renewable energy might incorporate physics (science), data analysis (math), circuit design (engineering), and programming sensors (technology).
- Robotics and AI: Introduction to basic robotics and artificial intelligence concepts.
- Data science literacy: Teaching students how to interpret and analyze data.
- Computational thinking: Developing problem-solving skills rooted in computer science.
- Green technology: Exploring sustainable solutions and environmental engineering.
These modules are meticulously crafted to be age-appropriate, scaling in complexity as students progress through K-12. The aim is to build a continuous learning pathway where each grade level reinforces and expands upon previously acquired knowledge.
Furthermore, the curriculum will incorporate digital tools and resources, ensuring that students are proficient in using modern technology for learning and problem-solving. This includes virtual labs, simulation software, and online collaborative platforms. The success of these components hinges on robust teacher training and ongoing professional development, ensuring educators are well-equipped to implement the new methodologies effectively. The holistic design of the 2026 STEM curriculum signifies a major leap forward in preparing students for a tech-driven future.
Funding and resource allocation for new programs
The ambitious scope of the new STEM education initiatives requires substantial financial backing and strategic resource allocation. Federal, state, and local governments, alongside private organizations, are committing significant funds to ensure these programs are successfully implemented across U.S. K-12 schools. This multi-faceted funding approach aims to create equitable access to high-quality STEM education for all students.
A significant portion of the funding will be directed towards teacher training and professional development. Equipping educators with the latest pedagogical techniques and subject matter expertise is crucial for the effective delivery of the new curriculum. Funds will also support the acquisition of advanced laboratory equipment, specialized software, and other technological resources essential for hands-on learning.
Government grants and partnerships
The federal government is playing a pivotal role through grants allocated to states and school districts. These grants often come with stipulations focused on promoting diversity in STEM, reaching underserved communities, and fostering innovative teaching practices. State governments are also supplementing these efforts with their own funding streams, often prioritizing regional STEM workforce needs.
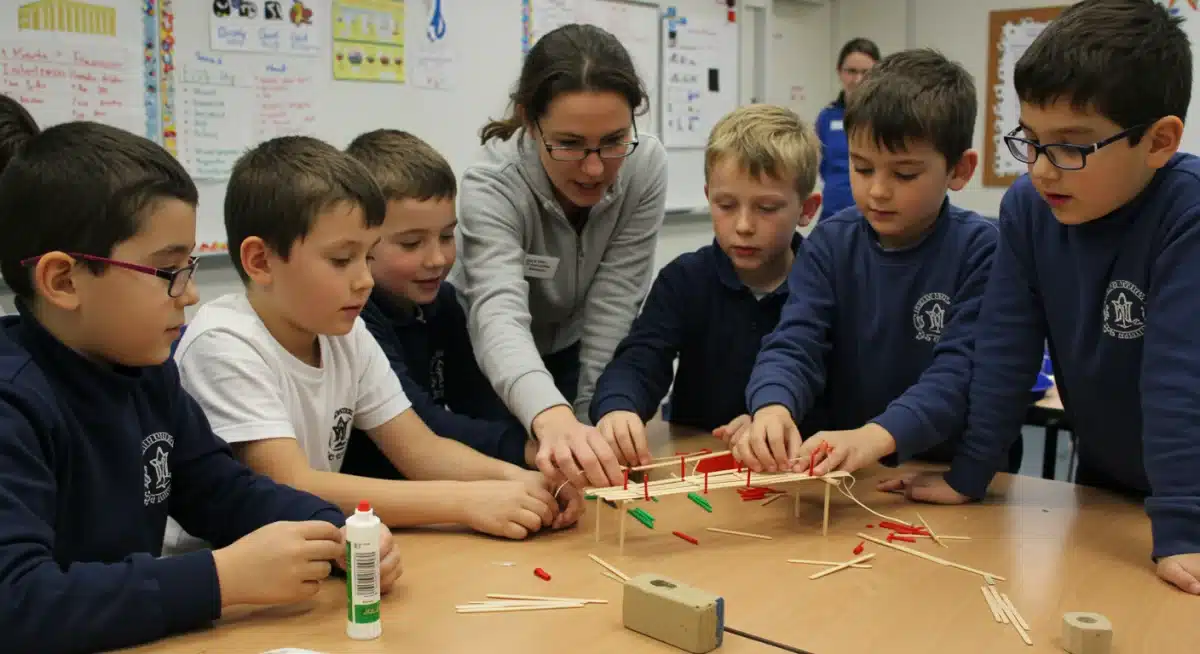


- Federal grants: Supporting widespread implementation and equity initiatives.
- State-level funding: Addressing specific regional educational and economic needs.
- Private sector partnerships: Companies investing in future talent and educational innovation.
Beyond direct financial aid, strategic partnerships with technology companies, universities, and non-profit organizations are providing valuable resources. These collaborations often involve mentorship programs, guest speakers, internships, and donations of equipment, enriching the learning experience for students.
The careful allocation of these resources is critical to ensuring that every school, regardless of its socioeconomic background, has the opportunity to implement these transformative STEM programs. This robust funding and resource model underscores the national commitment to elevating STEM education and preparing students for future success.
Teacher training and professional development
The success of any new educational initiative hinges on the preparedness and expertise of its educators. The new STEM education initiatives launching in 2026 place a strong emphasis on comprehensive teacher training and ongoing professional development. This ensures that teachers are not only proficient in the new curriculum but also skilled in employing innovative pedagogical approaches that foster deep learning and engagement.
Training programs will focus on equipping teachers with the knowledge and confidence to lead project-based learning activities, integrate technology effectively, and adapt lessons to meet diverse student needs. The goal is to transform classrooms into dynamic hubs of discovery and exploration, moving away from traditional lecture-based instruction.
New pedagogical approaches
Educators will receive training in cutting-edge teaching methodologies such as inquiry-based learning, computational thinking, and design thinking. These approaches encourage students to ask questions, experiment, and iterate solutions, mirroring the processes used by real-world scientists and engineers.
- Inquiry-based learning: Fostering student-led investigations and critical questioning.
- Computational thinking: Developing problem-solving strategies inspired by computer science.
- Design thinking: A human-centered approach to innovation, encouraging empathy and iteration.
Professional development will not be a one-time event but an ongoing process. Teachers will have access to workshops, online courses, and collaborative networks where they can share best practices and receive continuous support. This sustained investment in teacher growth is vital for maintaining the quality and relevance of STEM education over time.
Furthermore, partnerships with universities and industry experts will provide teachers with opportunities to engage directly with current research and technological advancements, ensuring their knowledge remains current. This robust framework for teacher training is a cornerstone of the 2026 STEM initiatives, guaranteeing that students benefit from highly skilled and motivated educators.
Equity and access in STEM education
A core principle guiding the new STEM education initiatives is the commitment to equity and access for all U.S. K-12 students. Historically, disparities in STEM education have existed, often disadvantaging students from underserved communities, girls, and minority groups. The 2026 programs are specifically designed to dismantle these barriers and ensure that every student has the opportunity to excel in STEM fields.
This focus on equity means providing targeted resources and support to schools in low-income areas, developing culturally responsive teaching materials, and actively promoting inclusivity in STEM classrooms. The aim is to foster an environment where all students feel empowered and encouraged to pursue their interests in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
Addressing underrepresentation
Initiatives will specifically target the underrepresentation of certain groups in STEM. This includes mentorship programs connecting students with diverse STEM professionals, scholarships for advanced STEM programs, and outreach efforts to spark interest early on. The goal is to broaden participation and ensure that the future STEM workforce reflects the diversity of the nation.
- Targeted outreach: Engaging underrepresented groups through specialized programs.
- Culturally responsive pedagogy: Tailoring teaching methods to diverse cultural backgrounds.
- Mentorship opportunities: Connecting students with diverse role models in STEM.
Furthermore, the curriculum development process is incorporating diverse perspectives to ensure that learning materials are relatable and inspiring to students from all backgrounds. This includes highlighting contributions from a wide range of scientists and engineers throughout history. By creating an inclusive and supportive learning environment, these initiatives seek to unlock the full potential of every student, regardless of their background.
The emphasis on equity and access is not just about fairness; it is about strengthening the entire STEM ecosystem by drawing on a wider pool of talent and perspectives. These concerted efforts promise to make STEM education truly accessible and enriching for all K-12 students across the United States.
Measuring impact and future outlook
As the new STEM education initiatives roll out in 2026, a critical component will be the rigorous measurement of their impact and effectiveness. Comprehensive evaluation frameworks are being developed to assess student outcomes, teacher efficacy, and the overall success of the programs in achieving their equity and educational goals. This data-driven approach will allow for continuous improvement and adaptation of the initiatives over time.
Metrics will extend beyond standardized test scores, encompassing indicators such as student engagement in STEM activities, participation in advanced STEM courses, and the development of critical 21st-century skills like problem-solving and collaboration. Feedback from students, teachers, and parents will also be integral to understanding the qualitative impact of the programs.
Long-term vision for STEM education
The long-term vision for STEM education in the U.S. is to cultivate a generation that is not only proficient in scientific and technological fields but also possesses the adaptive skills necessary to thrive in an ever-changing world. This includes fostering a lifelong love of learning and an ability to critically evaluate information.
- Student achievement: Tracking academic performance and skill development.
- Teacher effectiveness: Evaluating pedagogical impact and professional growth.
- Program equity: Assessing access and outcomes for all student demographics.
Beyond student achievement, the initiatives aim to strengthen the nation’s STEM workforce pipeline, ensuring a steady supply of innovators and researchers. The insights gained from ongoing evaluations will inform future policy decisions, curriculum updates, and resource allocation, ensuring that STEM education remains at the forefront of educational excellence. The commitment to continuous improvement underscores the transformative potential of these initiatives for U.S. K-12 students and the nation as a whole.
| Key Initiative | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Curriculum | New K-12 curriculum with integrated, hands-on, project-based STEM learning. |
| Funding & Resources | Significant federal, state, and private investment for equipment and program support. |
| Equity & Access | Programs designed to ensure all students, especially underrepresented groups, have access to high-quality STEM education. |
Frequently Asked Questions About New STEM Initiatives
The primary goals are to enhance critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and innovation among K-12 students. These initiatives aim to prepare students for future careers in STEM fields, bridge existing skills gaps, and foster a diverse, technologically proficient workforce for the United States.
These new STEM education opportunities are scheduled to begin for U.S. K-12 students starting in 2026. This timeline allows for comprehensive curriculum development, teacher training, and resource allocation to ensure a smooth and effective rollout across participating schools and districts.
Teacher training is a cornerstone of the new initiatives. Educators will receive extensive professional development in project-based learning, computational thinking, and other innovative pedagogies. This ensures they are well-equipped to deliver the new curriculum effectively and engage students in dynamic, hands-on STEM exploration.
Yes, a major focus is on equity and access. The initiatives include targeted efforts to support underserved communities, girls, and minority groups in STEM. This involves culturally responsive materials, mentorship programs, and resource allocation to ensure all students have equal opportunities to succeed in STEM fields.
Impact will be measured through a comprehensive framework including student academic performance, engagement in STEM activities, participation in advanced courses, and the development of 21st-century skills. Continuous evaluation and feedback from stakeholders will inform ongoing improvements and adaptations to the programs.
Conclusion
The upcoming STEM education initiatives represent a transformative moment for U.S. K-12 education. By prioritizing hands-on learning, integrated curricula, robust teacher development, and equitable access, these programs are set to empower a new generation of American students. The strategic investment in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics will not only prepare individuals for future career success but also strengthen the nation’s capacity for innovation and global competitiveness. As these opportunities unfold in 2026, the potential for a more skilled, curious, and inventive populace is immense, promising a brighter future for all.


 Federal Loan Forgiveness Programs: Key Updates for U.S. Professionals
Federal Loan Forgiveness Programs: Key Updates for U.S. Professionals  Top 6 In-Demand Certifications for U.S. Job Seekers
Top 6 In-Demand Certifications for U.S. Job Seekers  FAFSA Simplification Act: Essential Updates for College Applicants
FAFSA Simplification Act: Essential Updates for College Applicants