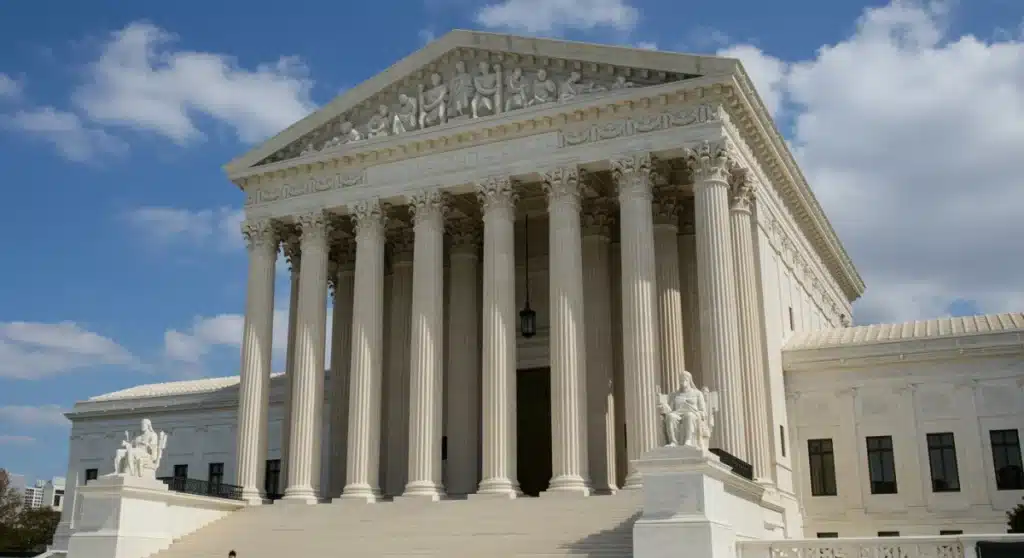
The Supreme Court is poised to issue significant decisions on a range of complex legal questions this term, with profound implications for constitutional interpretation and American society.
As the nation watches, the Supreme Court is currently deliberating on a series of pivotal cases that could redefine fundamental aspects of American law and society. The outcomes of these Upcoming Supreme Court Rulings are not just legal pronouncements; they are decisions that will ripple through communities, influence policy, and shape individual rights for years to come. Understanding these key cases is essential for any informed citizen.
Understanding the Supreme Court’s Role and Term
The Supreme Court of the United States stands as the highest judicial body in the federal government, tasked with interpreting the Constitution and federal laws. Its decisions are binding across the nation, making each term a critical period for legal observers and the public alike. The Court’s annual term typically begins on the first Monday in October and concludes in late June or early July, during which time it hears oral arguments, deliberates, and issues opinions on a select number of cases.
Each term, thousands of petitions for review are filed with the Court, but only a fraction—typically fewer than 100—are granted certiorari, meaning the Court agrees to hear the case. These chosen cases often involve significant constitutional questions, conflicts between lower courts, or issues of national importance that require a definitive ruling from the highest court.
The Selection Process: How Cases Reach the High Court
The process by which a case reaches the Supreme Court is intricate and highly selective. It usually begins with a petition for a writ of certiorari, requesting the Court to review a lower court’s decision. Four of the nine justices must agree to hear a case for it to be granted certiorari, a practice known as the “Rule of Four.”
- Conflict Among Circuits: Cases where federal circuit courts have issued conflicting rulings on similar legal issues.
- Constitutional Questions: Cases involving the interpretation of the U.S. Constitution or federal statutes.
- National Importance: Cases addressing issues of broad public or governmental significance.
Once a case is accepted, parties submit written briefs outlining their legal arguments, followed by oral arguments where attorneys present their cases directly to the justices. These arguments are often intense and highly scrutinized, offering a rare glimpse into the Court’s analytical process. The justices then deliberate in private conferences, eventually casting votes and assigning a justice to write the majority opinion, which sets the legal precedent.
The Court’s role extends beyond simply resolving disputes; it acts as a guardian of the Constitution, ensuring that laws passed by Congress and actions taken by the executive branch adhere to its principles. This makes every term a period of intense focus, as the Court’s decisions can profoundly alter the legal landscape and the lives of millions of Americans.
First Amendment Freedoms: Speech, Religion, and Assembly
The First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution guarantees several fundamental freedoms, including speech, religion, and assembly. These rights are often at the forefront of Supreme Court cases, as the Court continually grapples with their scope and limitations in an evolving society. This term, several cases touch upon these crucial liberties, testing the boundaries of expression and belief in modern contexts.
One notable area of contention often revolves around the intersection of religious freedom and anti-discrimination laws. The Court frequently hears cases that challenge the balance between an individual’s right to practice their religion freely and the state’s interest in preventing discrimination against protected classes. These cases are particularly complex, as they often pit deeply held beliefs against societal values of equality and inclusion.
Digital Speech and Online Expression
In the digital age, the concept of free speech has expanded to include online expression, presenting new challenges for legal interpretation. The Court is increasingly asked to consider how traditional First Amendment principles apply to the internet, social media platforms, and other digital forums. These cases often involve questions of content moderation, platform liability, and the extent to which online speech can be regulated without infringing on constitutional rights.
- Social Media Content Moderation: Cases examining whether government pressure on social media companies to remove certain content constitutes a violation of free speech.
- Online Defamation: Disputes over the legal responsibility of online platforms for user-generated content that may be defamatory or harmful.
- Digital Privacy and Expression: How privacy concerns intersect with the right to express oneself anonymously online.
Another significant aspect involves the right to protest and assembly, especially in the context of modern activism. The Court continues to define where and how individuals can lawfully gather to express their views, balancing these rights against public safety and order. The outcomes of these cases will have lasting implications for how individuals engage in public discourse and advocate for change.
The First Amendment remains a cornerstone of American democracy, and the Court’s rulings this term on speech, religion, and assembly will undoubtedly shape the future of these essential freedoms. These decisions will impact not only how individuals express themselves but also how institutions and governments interact with public discourse in an increasingly digital and diverse nation.
Voting Rights and Election Integrity
Voting rights are fundamental to the democratic process, ensuring that every eligible citizen has the opportunity to participate in elections. The Supreme Court has a long history of adjudicating disputes related to voting, from gerrymandering to voter ID laws. This term, the Court is again poised to address critical issues concerning election integrity and the accessibility of the ballot box, with potential ramifications for future elections.
Discussions around voting rights often center on the balance between ensuring fair and secure elections and preventing undue burdens on voters. Cases frequently arise from state-level legislation that seeks to modify voting procedures, such as changes to early voting, absentee ballot requirements, or voter registration processes. These legislative actions often become subjects of legal challenge, leading to Supreme Court review.
Gerrymandering and Fair Representation
Gerrymandering, the practice of drawing electoral district boundaries to give one political party an unfair advantage, remains a persistent challenge to fair representation. The Court has previously issued rulings on partisan gerrymandering, and this term may see further clarification on the extent to which courts can intervene in such political questions. The impact of these decisions can fundamentally alter the political landscape of states and the nation.
- Partisan Gerrymandering Challenges: Cases questioning the constitutionality of district maps drawn with explicit partisan intent.
- Racial Gerrymandering: Legal battles over district lines that dilute the voting power of minority groups.
- Independent Redistricting Commissions: Arguments for and against the role of non-partisan bodies in drawing electoral maps.
Another significant area involves the interpretation of the Voting Rights Act of 1965, a landmark piece of civil rights legislation. The Court has previously limited certain provisions of the Act, and new cases may further define its scope and effectiveness in protecting minority voting rights. The ongoing debate about federal oversight versus state control over elections is a central theme in many of these cases.
The integrity of elections is paramount for public trust in democratic institutions. The Supreme Court’s decisions on voting rights and election integrity this term will be closely watched, as they could reshape how Americans vote, how districts are drawn, and ultimately, who holds political power in the United States.
Environmental Regulations and Climate Policy
Environmental protection and climate policy have become increasingly critical issues, with significant legal battles often reaching the Supreme Court. These cases typically involve disputes between federal agencies, state governments, and private industries over the scope of environmental regulations and the authority to address climate change. The Court’s decisions in this area can have profound consequences for public health, economic development, and the nation’s response to global environmental challenges.
A recurring theme in environmental cases is the balance between economic development and ecological preservation. Industries often argue that stringent regulations impose undue financial burdens, while environmental groups contend that robust protections are necessary to prevent irreversible harm to the planet. The Supreme Court often acts as the arbiter in these complex disputes, interpreting statutes like the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act.

Agency Authority and the “Major Questions” Doctrine
Many environmental regulations are promulgated by federal agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This term, the Court may continue to scrutinize the extent of these agencies’ authority, particularly in light of the “major questions” doctrine. This doctrine suggests that Congress must clearly authorize agencies to regulate issues of vast economic and political significance, rather than allowing agencies to infer such authority from broad statutory language.
- EPA’s Authority to Regulate Emissions: Cases challenging the EPA’s power to set emissions standards for power plants and other industrial sources.
- Wetlands Protection: Disputes over the definition of “waters of the United States” and the extent of federal jurisdiction over wetlands under the Clean Water Act.
- Endangered Species Act Interpretations: Legal challenges concerning the application and enforcement of the Endangered Species Act in land use and development projects.
The Court’s approach to these environmental cases often reflects broader judicial philosophies regarding administrative law and the separation of powers. Decisions can either reinforce the ability of federal agencies to address complex environmental problems or place greater limits on their regulatory reach, potentially shifting more power to Congress or individual states.
As climate change continues to pose significant threats, the Supreme Court’s rulings on environmental regulations and climate policy are more critical than ever. These decisions will not only determine the future of environmental protection in the United States but also influence global efforts to combat climate change and preserve natural resources for future generations.
Healthcare Access and Policy Debates
Healthcare remains a contentious and vital area of law, frequently brought before the Supreme Court due to its profound impact on individuals and the economy. Cases related to healthcare access, insurance mandates, and regulatory frameworks often involve complex interpretations of federal statutes and constitutional principles. This term, the Court is expected to weigh in on several cases that could significantly alter the landscape of healthcare in the United States.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), often referred to as Obamacare, has been a recurring subject of legal challenges since its enactment. While many of its core provisions have been upheld, specific aspects or subsequent legislative amendments continue to face scrutiny. These cases often revolve around the extent of federal power to regulate healthcare, the rights of states, and the financial implications for individuals and providers.
Reproductive Rights and Access to Care
Reproductive rights, particularly those concerning abortion access, continue to be a highly charged and frequently litigated area. Following recent landmark decisions, states have increasingly enacted diverse laws regarding reproductive healthcare, leading to a patchwork of regulations across the country. The Supreme Court is often called upon to clarify the boundaries of these state laws and their consistency with federal constitutional protections.
- State-Level Abortion Bans: Challenges to laws that restrict or ban abortion at various stages of pregnancy.
- Access to Reproductive Healthcare Services: Cases concerning the availability of contraception and other reproductive health services.
- Medicaid Expansion Disputes: Legal challenges from states regarding the mandates and funding for Medicaid expansion under federal law.
Beyond reproductive rights, the Court also addresses broader issues of healthcare access for specific populations, including those with pre-existing conditions or those in rural areas. These cases often examine the role of federal and state governments in ensuring equitable access to medical care, as well as the responsibilities of insurance companies and healthcare providers.
The Supreme Court’s decisions on healthcare access and policy debates this term will have far-reaching consequences, influencing everything from insurance premiums and provider networks to individual medical choices. These rulings will continue to shape the ongoing national conversation about the right to healthcare and the government’s role in its provision.
Criminal Justice and Civil Liberties
Cases involving criminal justice and civil liberties are central to the Supreme Court’s docket each term, as they directly impact the rights of individuals accused of crimes and the powers of law enforcement. These cases often require careful balancing of public safety interests against constitutional protections, such as the Fourth Amendment’s guard against unreasonable searches and seizures, and the Sixth Amendment’s right to a fair trial.
The Court frequently reviews issues related to police conduct, including the use of force, interrogation techniques, and the admissibility of evidence obtained through various investigative methods. These decisions establish precedents that guide police departments nationwide and define the boundaries of legitimate law enforcement action, ensuring that individual freedoms are respected within the criminal justice system.
Fourth Amendment Protections in the Digital Age
With the rapid advancement of technology, the application of Fourth Amendment protections against unreasonable searches and seizures has become increasingly complex. The Court is often asked to determine how these protections apply to digital data, electronic surveillance, and the use of new technologies by law enforcement. These cases aim to strike a balance between effective crime fighting and safeguarding individual privacy in an era of pervasive digital footprints.
- Warrantless Searches of Digital Devices: Cases assessing whether law enforcement needs a warrant to search smartphones, computers, or other electronic devices.
- Geofence Warrants: Challenges to the use of warrants that compel tech companies to provide data on all devices within a specific geographic area during a particular time.
- Biometric Data Collection: Disputes over the collection and use of biometric data, such as fingerprints or facial scans, by government agencies.
Another crucial aspect of criminal justice cases involves the rights of defendants, including the right to adequate legal representation and protection against cruel and unusual punishment. The Court’s interpretations of these rights can significantly affect the fairness of trials, sentencing practices, and the overall integrity of the justice system. The outcomes of these cases often reflect societal values regarding punishment, rehabilitation, and the pursuit of justice.
The Supreme Court’s rulings on criminal justice and civil liberties this term will have a profound impact on how law enforcement operates and how individual rights are protected within the American legal system. These decisions are vital for maintaining the delicate equilibrium between public safety and the fundamental freedoms guaranteed to all citizens.
Business and Economic Regulation
The Supreme Court plays a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of the United States through its decisions on business and economic regulation. Cases in this area often involve complex questions of corporate power, consumer protection, antitrust law, and the extent of governmental authority to regulate commerce. The Court’s rulings can have significant financial implications for industries, investors, and consumers across the nation.
A common theme in these cases is the interpretation of federal statutes designed to regulate markets and prevent monopolies. Antitrust laws, for instance, are frequently challenged, with businesses arguing for less governmental intervention and consumer advocates pushing for stronger protections against anti-competitive practices. The Court’s approach to these issues helps define the competitive environment for various sectors of the economy.
Consumer Protection and Corporate Liability
Consumer protection is another significant aspect of economic regulation that regularly comes before the High Court. Cases often involve disputes over product liability, deceptive marketing practices, and the enforceability of consumer contracts. The Court’s decisions in this domain can empower consumers to seek redress for harm or limit corporate accountability, depending on its interpretation of relevant laws.
- Class Action Lawsuits: Cases determining the scope and viability of class action lawsuits against corporations for various harms.
- Arbitration Agreements: Disputes over the enforceability of mandatory arbitration clauses in consumer and employment contracts.
- Financial Regulations: Challenges to the authority of federal agencies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), to regulate financial markets and protect investors.
Furthermore, the Court often addresses issues related to federal agency deference, particularly concerning economic regulations. The “Chevron deference” doctrine, which traditionally grants deference to an agency’s reasonable interpretation of an ambiguous statute it administers, has been a subject of ongoing debate. Any changes to this doctrine could significantly alter the regulatory power of federal agencies and the stability of existing economic rules.
The Supreme Court’s forthcoming decisions on business and economic regulation are crucial for understanding the future direction of American commerce. These rulings will influence everything from corporate governance and market competition to consumer rights and the overall regulatory environment, impacting businesses and individuals alike.
| Key Case Area | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| First Amendment Freedoms | Redefines scope of speech, religion, and assembly rights, especially online. |
| Voting Rights | Shapes electoral processes, including gerrymandering and voter access. |
| Environmental Regulations | Determines federal agency power over climate policy and environmental protection. |
| Healthcare Access | Influences insurance coverage, reproductive rights, and medical service availability. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Supreme Court Rulings
A Supreme Court ruling sets a binding legal precedent for all lower federal and state courts. These decisions interpret the U.S. Constitution and federal laws, profoundly impacting American society, government, and individual rights across the nation.
Out of thousands of petitions, the Supreme Court typically hears fewer than 100 cases each term. This selective process ensures that only cases with significant legal or constitutional questions reach the highest court for a definitive ruling.
The “Rule of Four” is a Supreme Court practice requiring at least four of the nine justices to agree to hear a case before it is granted certiorari. This rule allows a minority of the Court to bring cases of national importance to the full Court for review.
Supreme Court rulings can directly impact everyday Americans by shaping laws concerning civil rights, healthcare, environmental protection, voting, and economic regulations. These decisions define legal boundaries and individual freedoms that govern daily life.
The Supreme Court’s annual term officially begins on the first Monday in October. It typically concludes in late June or early July of the following year, with major opinions often released towards the end of the term.
Conclusion
The current Supreme Court term is proving to be a period of intense legal activity, with a diverse array of cases touching upon the most pressing issues facing the United States. From the nuanced interpretations of First Amendment freedoms in the digital age to the foundational questions surrounding voting rights and environmental policy, each impending decision carries significant weight. These Upcoming Supreme Court Rulings will not merely resolve legal disputes; they will establish precedents that guide future legislation, administrative actions, and societal norms, directly influencing the lives of millions. Staying informed about these key cases is crucial for understanding the evolving legal landscape and the direction our nation is heading. As the Court continues its deliberations, the anticipation for these landmark decisions underscores the enduring power and influence of the judiciary in shaping the American experiment.


 U.S. Unemployment Rate Holds at 3.9%: Economic Stability Persists
U.S. Unemployment Rate Holds at 3.9%: Economic Stability Persists  Federal Reserve Interest Rate Decision: U.S. Mortgage Impact
Federal Reserve Interest Rate Decision: U.S. Mortgage Impact  Auto industry slowdown jobs impact US economy
Auto industry slowdown jobs impact US economy