The U.S. unemployment rate has consistently remained at 3.9% for the third consecutive month, signaling a notable period of stability within the American labor market and providing key insights into the broader economic landscape.
Have you been keeping an eye on the latest economic news? The fact that the U.S. unemployment rate holds at 3.9% for the third consecutive month is more than just a statistic; it’s a significant indicator of the current health and future direction of the American economy. This sustained level of unemployment offers both reassurance and points of discussion for policymakers, businesses, and everyday citizens alike, prompting us to delve deeper into what this stability truly signifies.
Understanding the Consistent 3.9% Unemployment Rate
The consistent maintenance of the U.S. unemployment rate at 3.9% for three consecutive months is a noteworthy economic phenomenon. This stability suggests a labor market that is neither overheating nor significantly contracting, providing a sense of equilibrium that many economists find encouraging. It points to a resilient economy capable of absorbing shocks and maintaining a steady course.
This sustained rate is particularly interesting when viewed through the lens of recent economic fluctuations. After periods of volatility, a flat unemployment rate can be interpreted as the labor market finding its footing, indicating that job creation and job separations are largely in balance. It’s a critical figure for assessing the effectiveness of monetary and fiscal policies.
Analyzing Key Labor Market Indicators
Beyond the headline number, several underlying indicators contribute to this stable unemployment figure. These include factors such as labor force participation, job openings, and wage growth, all of which paint a more complete picture of the market’s dynamics.
- Labor Force Participation: While the unemployment rate holds steady, changes in who is actively seeking work can influence the overall perception of the market’s strength. A stable participation rate alongside low unemployment suggests a healthy engagement in the job market.
- Job Openings: A high number of job openings, even with a stable unemployment rate, can indicate a persistent demand for workers, potentially leading to future wage pressures or continued growth.
- Wage Growth: Moderate wage growth accompanying stable unemployment suggests that employers are competing for talent without sparking excessive inflation, a delicate balance policymakers strive to achieve.
In essence, the 3.9% figure is not an isolated metric but a reflection of a complex interplay of forces within the labor market. Its consistency over time provides a valuable benchmark for economic analysis and future projections.
Implications for the American Economy
A stable U.S. unemployment rate holds at 3.9% for the third consecutive month carries profound implications for the broader American economy. This sustained low rate often correlates with consumer confidence, spending patterns, and overall economic growth. When unemployment remains low, more people are earning income, which typically translates into increased consumer demand and business activity.
This period of stability can also influence investment decisions. Businesses are more likely to expand and invest in new projects when they perceive a reliable labor supply and sustained consumer purchasing power. This creates a positive feedback loop, fostering further job creation and economic vitality. However, it also raises questions about potential inflationary pressures if demand consistently outstrips supply.
Impact on Inflation and Monetary Policy
The relationship between a low unemployment rate and inflation is a perennial concern for central banks. A tight labor market, where there are more jobs than available workers, can lead to upward pressure on wages, which in turn can contribute to higher prices for goods and services.
- Federal Reserve’s Stance: The Federal Reserve closely monitors the unemployment rate as a key indicator for its monetary policy decisions. A stable, low rate might suggest the economy is operating near full employment, potentially influencing decisions on interest rates.
- Wage-Price Spiral Concerns: While not currently a dominant concern, a prolonged period of low unemployment could, in theory, contribute to a wage-price spiral if unchecked. However, current data often shows wage growth remaining within manageable levels.
- Consumer Purchasing Power: Stable employment combined with moderate wage increases can boost consumer purchasing power, but if inflation outpaces wage growth, real incomes could decline, impacting overall economic health.
Ultimately, the consistent 3.9% unemployment rate presents a nuanced challenge for policymakers. It signals a robust labor market but also necessitates careful monitoring to prevent the emergence of destabilizing inflationary trends.
Sector-Specific Performance and Job Growth
While the national U.S. unemployment rate holds at 3.9% for the third consecutive month, a closer look reveals varying performance across different sectors of the economy. Not all industries contribute equally to this overall stability, and understanding these nuances is crucial for a comprehensive economic picture. Some sectors may be experiencing robust growth and high demand for labor, while others might be facing stagnation or even contraction.
This differential performance highlights the dynamic nature of the American job market. Emerging industries often drive significant job creation, while established sectors might see more moderate growth or shifts in employment patterns due to technological advancements or changing consumer preferences. Analyzing these sector-specific trends helps identify where economic strengths and potential vulnerabilities lie.
Leading and Lagging Industries
Certain sectors consistently lead in job growth, contributing disproportionately to the overall stability of the unemployment rate. Conversely, some industries might be struggling, indicating areas that require attention or adaptation.
- Technology and Innovation: The tech sector, including software development, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity, continues to be a strong engine for job creation, often demanding specialized skills.
- Healthcare and Social Assistance: Driven by an aging population and ongoing healthcare needs, this sector consistently adds jobs across various roles, from direct care to administrative support.
- Manufacturing and Construction: These sectors often show cyclical patterns, but recent data might indicate steady, albeit not explosive, growth, supported by infrastructure projects and domestic demand.
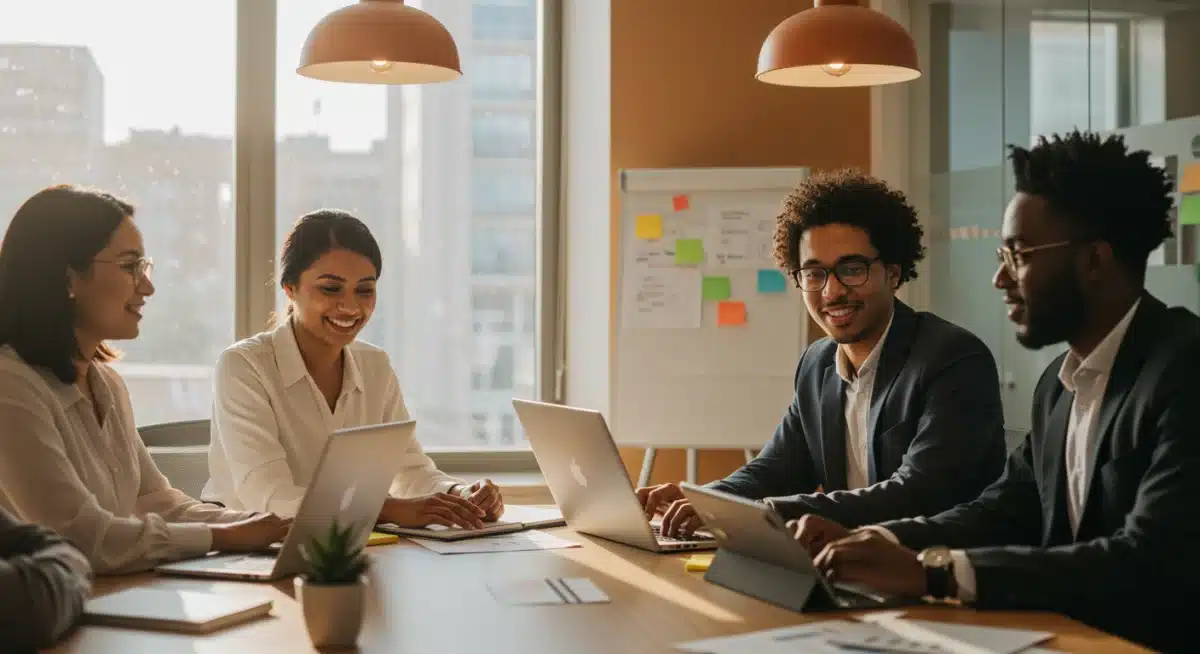

Understanding these sector-specific contributions is vital for policymakers to tailor educational and workforce development programs, ensuring that the labor force can meet the evolving demands of the economy. The stable national rate masks these important underlying shifts.
Regional Disparities in Employment
Even with the national U.S. unemployment rate holds at 3.9% for the third consecutive month, it is important to acknowledge that employment conditions are not uniform across all regions of the United States. Economic landscapes vary significantly from state to state and even within different metropolitan areas, influenced by local industries, demographics, and policy environments. A low national average can sometimes obscure higher unemployment rates in specific localities or states, indicating localized economic challenges.
These regional disparities are often tied to the dominant industries in a particular area. For instance, regions heavily reliant on a single industry might experience greater fluctuations in their local unemployment rates if that industry faces headwinds. Conversely, diversified economies tend to exhibit more stable employment figures. Understanding these geographical differences is crucial for targeted economic development efforts and social support programs.
Factors Contributing to Regional Differences
Several factors contribute to the varied employment pictures across the nation, even when the overall national rate remains stable. These factors range from industry concentration to demographic shifts and access to education.
- Industry Concentration: Regions with a high concentration of a specific industry (e.g., automotive in Michigan, technology in California) often see their local employment rates rise and fall with the fortunes of that sector.
- Population Migration: Inward or outward migration patterns can significantly impact the local labor supply and demand, affecting unemployment rates in distinct ways.
- Educational Attainment: Areas with higher levels of educational attainment and specialized skills training often have lower unemployment rates, as their workforce is better equipped to adapt to evolving job market demands.
Therefore, while the 3.9% national figure provides a broad overview, a deeper dive into regional data is essential to identify areas that might still require specific interventions to improve employment opportunities and economic well-being.
The Role of Government Policy and Economic Outlook
The sustained period where the U.S. unemployment rate holds at 3.9% for the third consecutive month is not solely a result of market forces; government policies play a significant role in shaping the labor landscape. Fiscal policies, such as government spending and taxation, alongside monetary policies set by the Federal Reserve, are designed to influence economic activity, including employment levels. These interventions can either stabilize or disrupt market trends, making their consideration crucial in understanding current economic conditions.
Moreover, the economic outlook for the coming months and years is heavily influenced by how these policies are perceived and adjusted. Businesses and consumers make decisions based on their expectations of future economic stability, which in turn feeds back into employment figures. A consistent unemployment rate, therefore, often reflects a period where current policies are seen as generally effective in maintaining economic balance, or at least not actively hindering it.
Future Projections and Potential Challenges
Despite the current stability, economists and policymakers are constantly looking ahead, anticipating future trends and potential challenges that could impact the unemployment rate. This forward-looking approach helps in preparing for economic shifts.
- Interest Rate Adjustments: Future decisions by the Federal Reserve regarding interest rates could either stimulate or cool down economic activity, directly impacting job growth and the unemployment rate.
- Global Economic Headwinds: International economic events, such as geopolitical tensions or slowdowns in major trading partners, can ripple through the U.S. economy, potentially affecting employment.
- Technological Disruption: Ongoing advancements in automation and artificial intelligence could lead to shifts in labor demand, requiring continuous adaptation of the workforce and new job creation strategies.
In conclusion, the consistent 3.9% unemployment rate is a testament to a period of relative economic stability, but it also underscores the ongoing need for vigilant policy-making and strategic planning to navigate future economic complexities.
Impact on Personal Finances and Career Planning
For individuals, the news that the U.S. unemployment rate holds at 3.9% for the third consecutive month has direct and tangible implications for personal finances and career planning. A stable and low unemployment rate generally signifies a healthier job market, which can translate into greater job security, more opportunities for career advancement, and potentially better wage growth. This environment can empower individuals to make more confident financial decisions, from saving for retirement to making large purchases.
Conversely, even a stable low rate means that some individuals are still seeking employment. For those actively in the job market, understanding the dynamics of this stable rate can inform their job search strategies. It suggests that while opportunities exist, competition for desirable roles may still be present, emphasizing the importance of skill development and strategic networking.
Navigating a Stable Job Market
In a stable job market, both job seekers and those currently employed can leverage the consistent unemployment rate to their advantage. It offers a window of opportunity for growth and financial improvement.
- Skill Development: With consistent demand, investing in new skills or certifications can make individuals more competitive and open doors to higher-paying positions.
- Negotiating Power: A tight labor market can give employees more leverage in negotiating salaries and benefits, especially in high-demand fields.
- Financial Planning: Increased job security and potential for wage growth can encourage more aggressive financial planning, including debt reduction, investment, and building emergency funds.
Ultimately, the consistent 3.9% unemployment rate provides a backdrop of general economic health that, when understood, can be strategically used by individuals to enhance their personal financial well-being and career trajectories.
Historical Context and Future Outlook of U.S. Unemployment
Placing the current situation where the U.S. unemployment rate holds at 3.9% for the third consecutive month into historical context offers valuable perspective. Historically, an unemployment rate below 4% is often considered indicative of a strong, near full-employment economy. Periods of such sustained low unemployment are relatively rare and usually follow significant economic recovery or robust growth phases. Understanding this historical backdrop helps us appreciate the significance of the current stability and its potential longevity.
Looking back at past economic cycles, periods of low unemployment have sometimes preceded inflationary pressures or policy adjustments designed to cool the economy. Conversely, prolonged periods of low unemployment without significant inflation suggest a ‘Goldilocks’ scenario – an economy that is neither too hot nor too cold. This historical lens informs current discussions about the sustainability of the present economic conditions.
Forecasting Future Trends
While the present is stable, the future of the U.S. unemployment rate is subject to various influences. Economic forecasts consider a multitude of factors to predict where the rate might head in the coming quarters and years.
- Demographic Shifts: Changes in birth rates, immigration, and retirement patterns can alter the size and composition of the labor force, impacting the natural rate of unemployment.
- Technological Advancements: The acceleration of automation and artificial intelligence could continue to reshape job roles, potentially leading to short-term displacement but also creating new opportunities.
- Global Economic Integration: The interconnectedness of global markets means that economic events in other parts of the world can influence U.S. employment trends, either positively or negatively.
In summary, the consistent 3.9% unemployment rate is a significant marker of current economic health. However, a comprehensive understanding requires both a historical perspective and a forward-looking analysis of the factors that will shape the labor market’s future.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Rate Stability | The U.S. unemployment rate held steady at 3.9% for three consecutive months, indicating strong labor market equilibrium. |
| Economic Implications | This stability suggests sustained consumer spending, business investment, and a resilient economy, though inflation concerns remain. |
| Sector Performance | Job growth varies by sector, with tech and healthcare often leading, while regional disparities highlight localized economic conditions. |
| Future Outlook | Government policies, global events, and technological shifts are key in shaping future unemployment trends and economic stability. |
Frequently Asked Questions About U.S. Unemployment
A 3.9% unemployment rate generally indicates a strong and healthy labor market, often considered near full employment. It suggests that most individuals who are willing and able to work have found jobs, contributing to economic stability and consumer confidence.
Consistent low unemployment typically boosts consumer confidence and spending. With more people employed and earning stable incomes, they are more likely to make purchases, invest, and contribute to overall economic growth, creating a positive cycle.
While generally positive, a sustained low unemployment rate can sometimes lead to inflationary pressures. A tight labor market can drive up wages, which businesses might pass on to consumers through higher prices for goods and services.
Government fiscal and monetary policies significantly influence the unemployment rate. Measures like interest rate adjustments by the Federal Reserve, government spending, and tax policies are designed to either stimulate or cool down economic activity, thereby affecting job creation.
A stable low unemployment rate generally creates a favorable environment for career planning. It suggests more job opportunities, potential for wage growth, and increased job security, empowering individuals to pursue skill development and negotiate better terms.
Conclusion
The consistent report that the U.S. unemployment rate holds at 3.9% for the third consecutive month paints a picture of remarkable stability and resilience within the American labor market. This sustained low rate is a testament to an economy that, despite various global and domestic challenges, has found a sturdy footing. It suggests a balance between job creation and labor demand, fostering an environment conducive to consumer confidence and business investment. While broad economic indicators point to health, a deeper dive reveals nuanced sector-specific performances and regional disparities that continue to shape local economies. Looking ahead, the interplay of government policies, technological advancements, and global economic shifts will be crucial in maintaining this equilibrium and navigating future challenges. For individuals, this stable outlook offers a strong foundation for career growth and personal financial planning, highlighting the importance of adaptability and continuous skill development in a dynamic job market.

 Federal Reserve Interest Rate Decision: U.S. Mortgage Impact
Federal Reserve Interest Rate Decision: U.S. Mortgage Impact  Auto industry slowdown jobs impact US economy
Auto industry slowdown jobs impact US economy  Pentagon’s Cyber Defense: New Strategies for 2025 Unveiled
Pentagon’s Cyber Defense: New Strategies for 2025 Unveiled